FlowWright AI Copilot, designed with user-friendliness in mind, functions much like the Windows copilot. It allows users to effortlessly pose questions based on FlowWright data, empowering them to delve deeper into their data analysis.
Copilot offers the following features:
- Answer generic questions based on a master data set, summary data
- Answer questions based on context, based on what page and what data is selected
- Designer predictions
Examples of generic questions:
- # of total open tasks
- # of total completed tasks
- # of process definitions
- # of process instances
Examples of context-based questions:
- Definitions page
- Who has the most # of definitions
- Who is most active
- What definitions with the highest # of instances
- What definitions haven’t been updated in the last one year
- Selected process definition
- What is the list of tasks
- # of steps
- Give a summary of the process
- Selected process instance
- What’s the longest step
- What users are involved
Examples of designer-based questions:
- Process Designer
- Suggest and build a diagram based on a question like “Create a change control process.”
- Given the current step, guess the next couple of steps
- Take the last # of steps before the current step and predict the next # of steps
- Forms Designer
- Provide a question for a form; AI automatically builds the form
AI Configuration Settings
There are two modes of operation: Online and Local.
OpenAI will use the online OpenAI service, and FlowWright will communicate with OpenAI through the rest of the services and provide the result.
For the Local mode, the LLM will be downloaded to the local server and used for AI services.
The configuration will be as follows: You'll have to navigate to Status—Settings—AI Copilot. You may select Online, Local, or Turn Off the AI Copilot feature here.
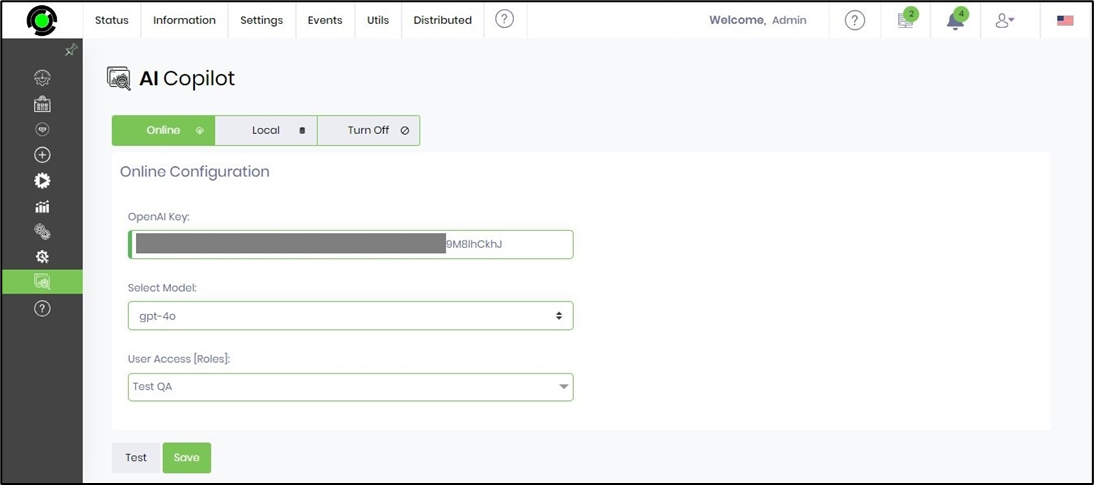
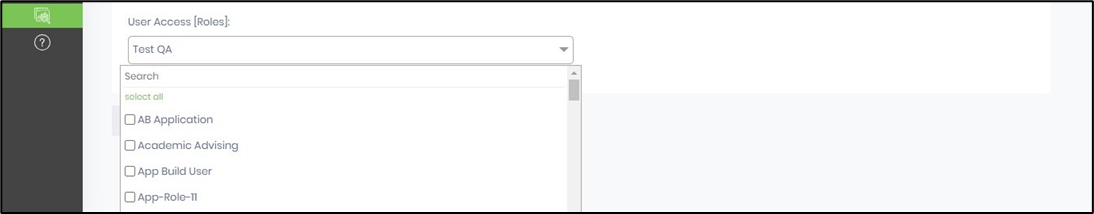
For Online OpenAI service, select Online mode and provide the OpenAI license key. Select one of the models from the drop-down list (gpt-4o or gpt-3.5-turbo). Select the User Access by checking the application roles from the multi-checkbox list. Click on the Save button to confirm the settings.
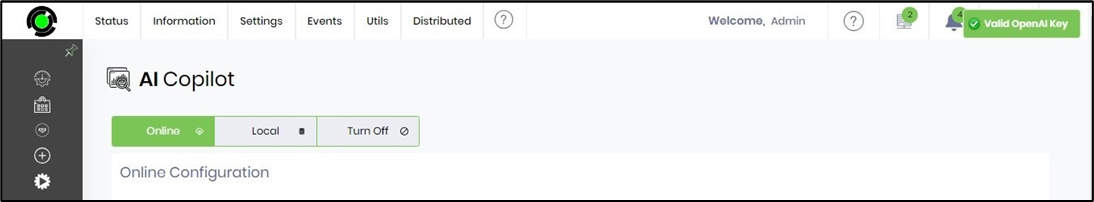
Click on the Test button to verify the configuration. A confirmation message is displayed in the top right corner.
For Local AI service, choose Local mode and select one of the models from the drop-down list (ggml-model-IQ3_M.gguf or mmproj-model-f16.gguf). Select the User Access by checking the application roles from the multi-checkbox list. Click on the Save button to confirm the settings.
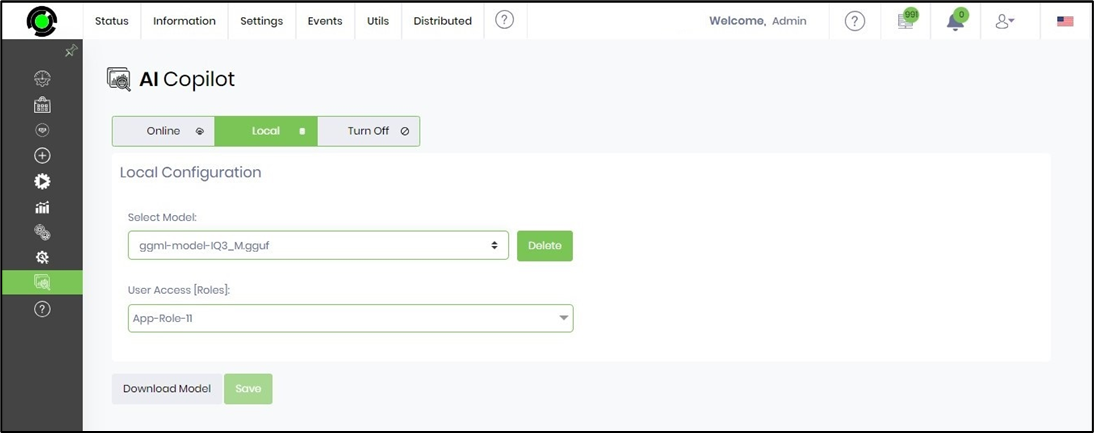
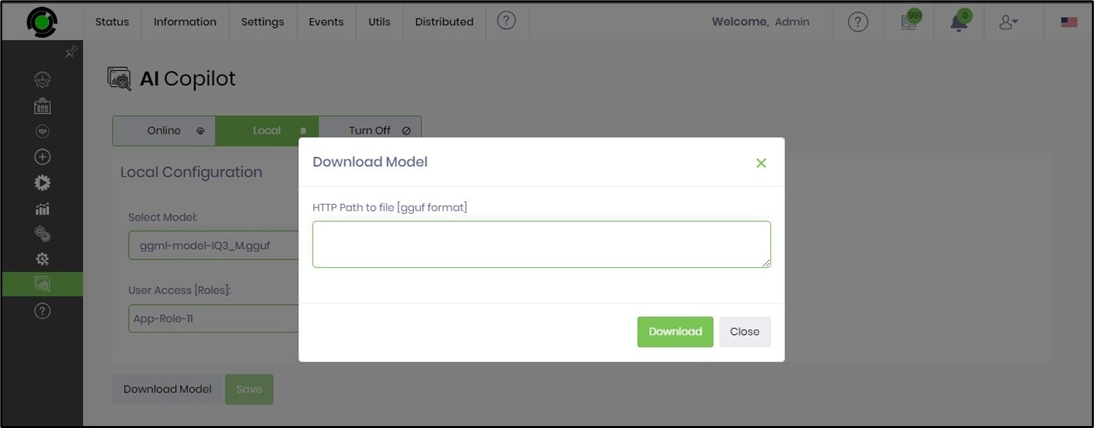
Click the Download Model button to download the LLM model to the local server. Provide the HTTP path and select the Download button to initiate the activity. Note: Verify there’s 10GB of space to accommodate the download file.
To turn the AI Copilot, select the button and click on Save to confirm.
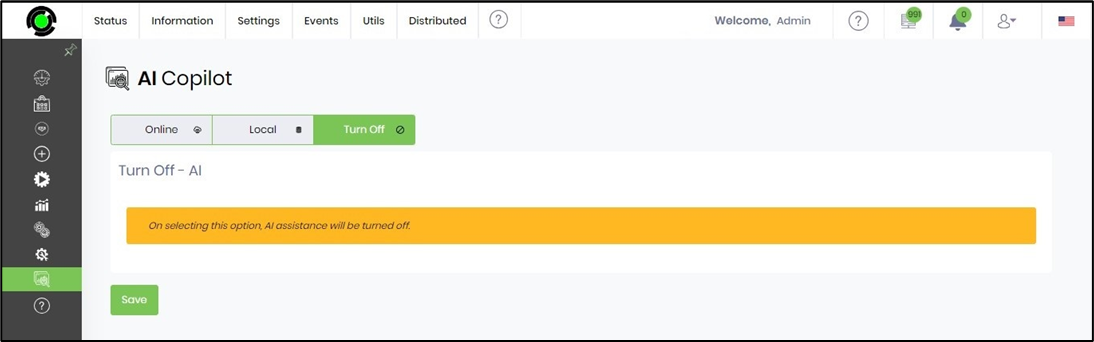
NOTE: We can only disable the Copilot in certain areas based on the roles configured for access.
Page Copilot User Interface
The following features of FlowWright provide a Page Copilot User Interface.
- Tasks
- Process Definitions
- Process Instances
- Form Definitions
- Form Instances
Create Process - Copilot UI
On the Process Definition page, select the Copilot—Create Process menu. If this function is not visible, you may have to check the Status—Settings—AI Copilot page.
A popup is displayed for configuration. Provide a process name and describe the process in a few words, as shown below. Click on the Generate Steps button.
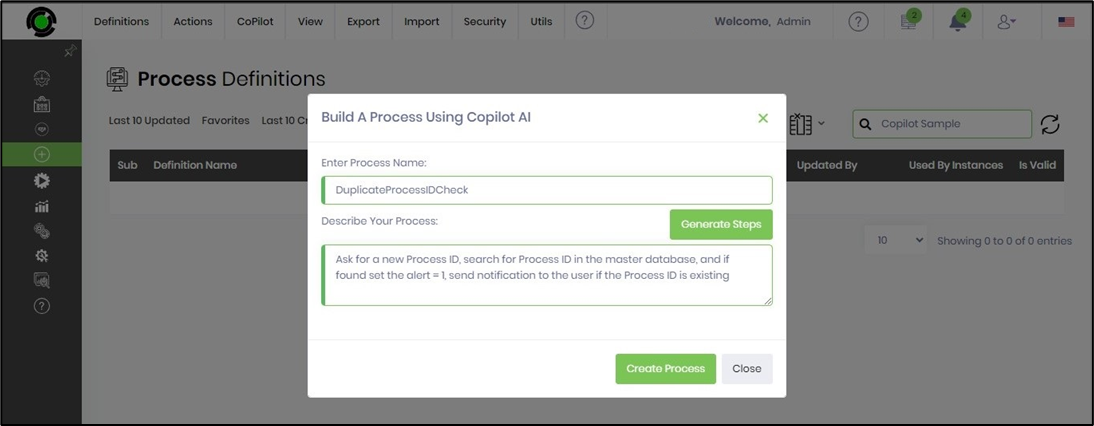
The predicted steps are generated and arranged as a list of checkboxes as below. You may uncheck the list item if it's irrelevant. Click on the Generate Process step when ready.
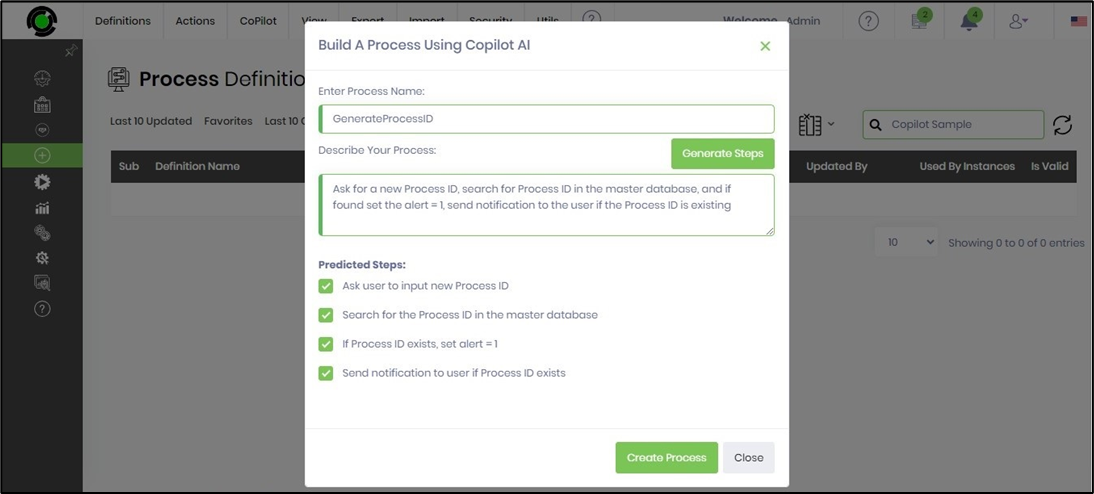
The AI Copilot prepares a new process definition and a workflow that matches the predicted steps. It would be best if you had to define the variables/globals to use in the process. You can modify the workflow to include other process steps to enhance the functionality. Click on the Save menu option to confirm the changes.
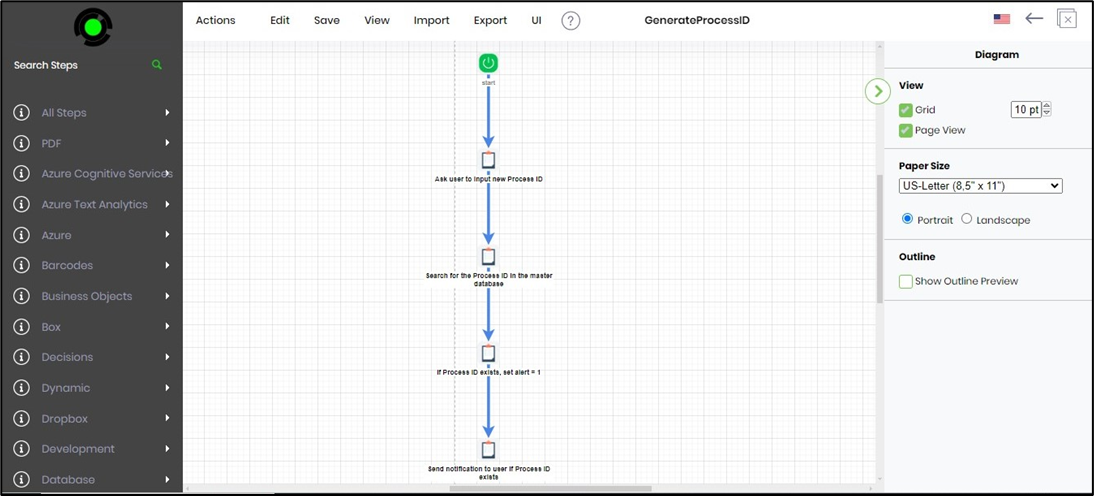
Process Designer - Predict new steps
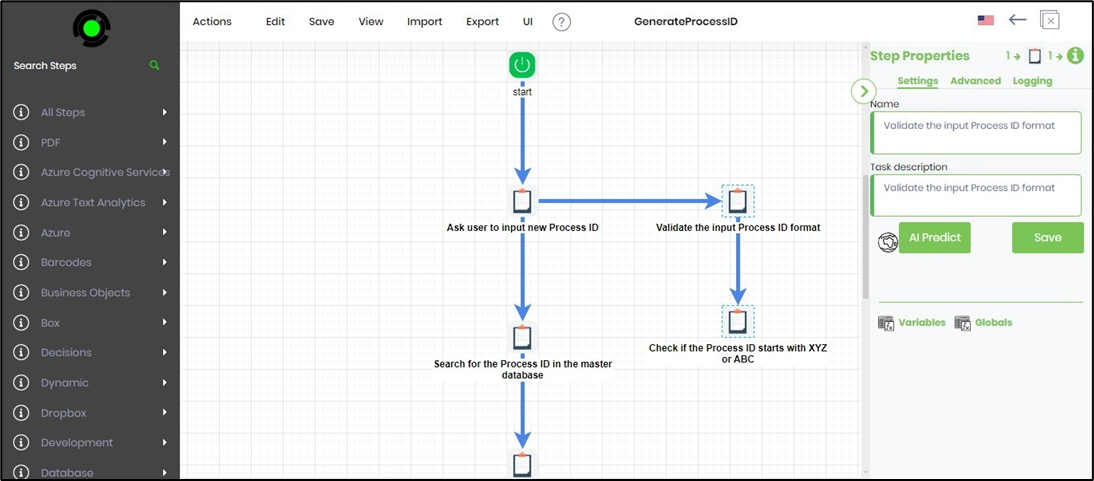
You may also use the AI Predict feature by selecting any process steps.
As shown below, the Task step is selected to use the AI Predict feature on the Step Properties pane. You may include a few more this way as necessary.
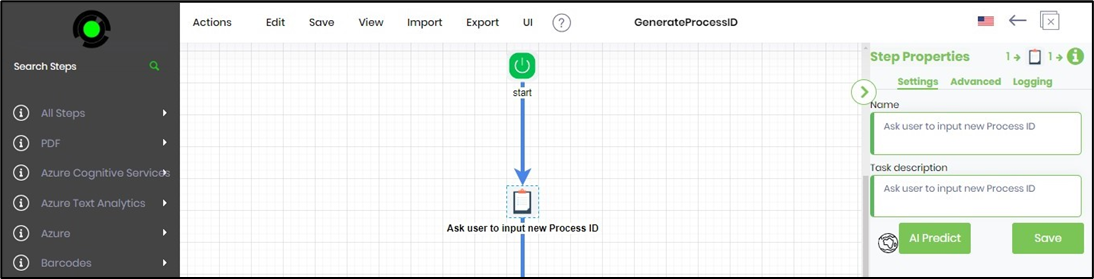
A popup window is displayed as below. Provide the number of steps to generate, with three steps being the minimum. Describe the new steps. Click the Predict button when ready.
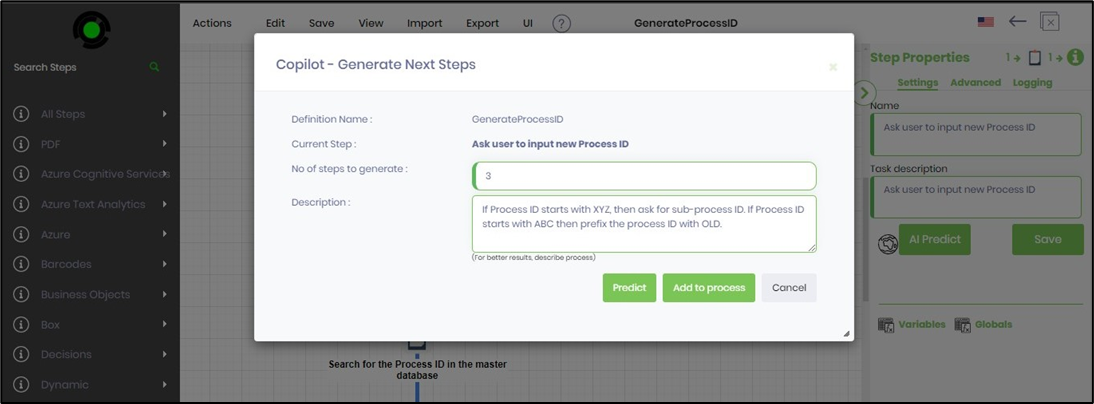
The new predicted steps are generated and arranged as a list of checkboxes as below. You may uncheck the list item if it's irrelevant. Click on the Add to Process button when ready.
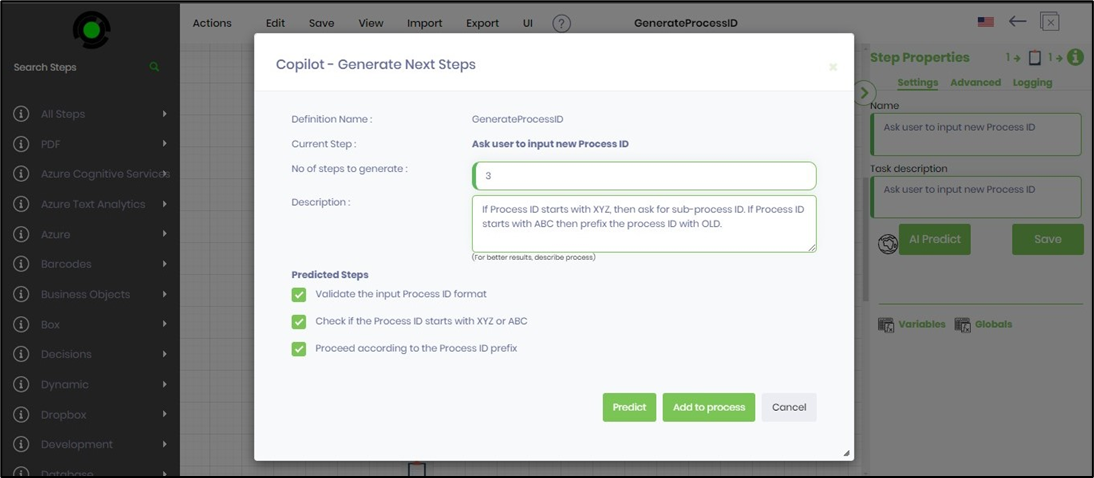
The AI Copilot modifies the process definition by including the new predicted steps in the workflow. It would be best if you had to define the new variables/globals to use in the modified process. Click on the Save menu option to confirm the workflow.