Description:
This step creates and initializes an environment variable on the application server.
Inputs
- name – provide a step name
- envvarmappings – environmental variable mappings
Returns
- True – step executed successfully
- False – step failed to execute
Usage:

Example:
Let’s build and execute the “setEnvironmentVariablesDef” example.
- Create a new definition called “setEnvironmentVariablesDef” and open the definition in designer mode.
- Drag a “setEnvironmentVariables” step and a “readEnvironmentVariables” step to the canvas.
- Connect the dots between the “Start” and other steps, as shown above
- Define a variable or a global to store the result.
- Click the "setEnvironmentVariables" step to configure its "Required" properties. Provide a name for the step. Click the button to configure environment variable mappings. Click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button for the Copilot to add new process steps that match your process description.

- A pop-up window appears for configuration. Click the Add Row button to insert an empty row. Enter the environment variable and its value. Click the Save button. You may add multiple environment variables using the Add Row button.

- The “Logging” configuration is necessary for documentation and also measures workflow progress and percent complete. This is achieved by configuring the step state and percent fields individually, as shown in the images below. Configure the “Logging” using the following properties.

- Click the "readEnvironmentVariables" step to configure its "Required" properties. Provide a name for the step. Click the button to configure environmental variable mappings, then click Save. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button for the Copilot to add new process steps that match your process description.

- A pop-up window appears for configuration. Click the Add Row button to insert an empty row. Enter the environment variable and its value. Click the Save button. You may add multiple environment variables using the Add Row button.

- The “Logging” configuration is necessary for documentation and also measures workflow progress and percent complete. This is achieved by configuring the step state and percent fields individually, as shown in the images below. Configure the “Logging” using the following properties.

- Save the process definition, create a new instance, and execute it. Render the process instance. Click the “readEnvironmentVariables” process step to view its properties. The step should retrieve the environment variable value set by the “setEnvironmentVariables” process step.
Create or modify environment variables on Windows 10:
- On the Windows taskbar, right-click the Windows icon and select System.
- In the Settings window, under Related Settings, click Advanced system settings.
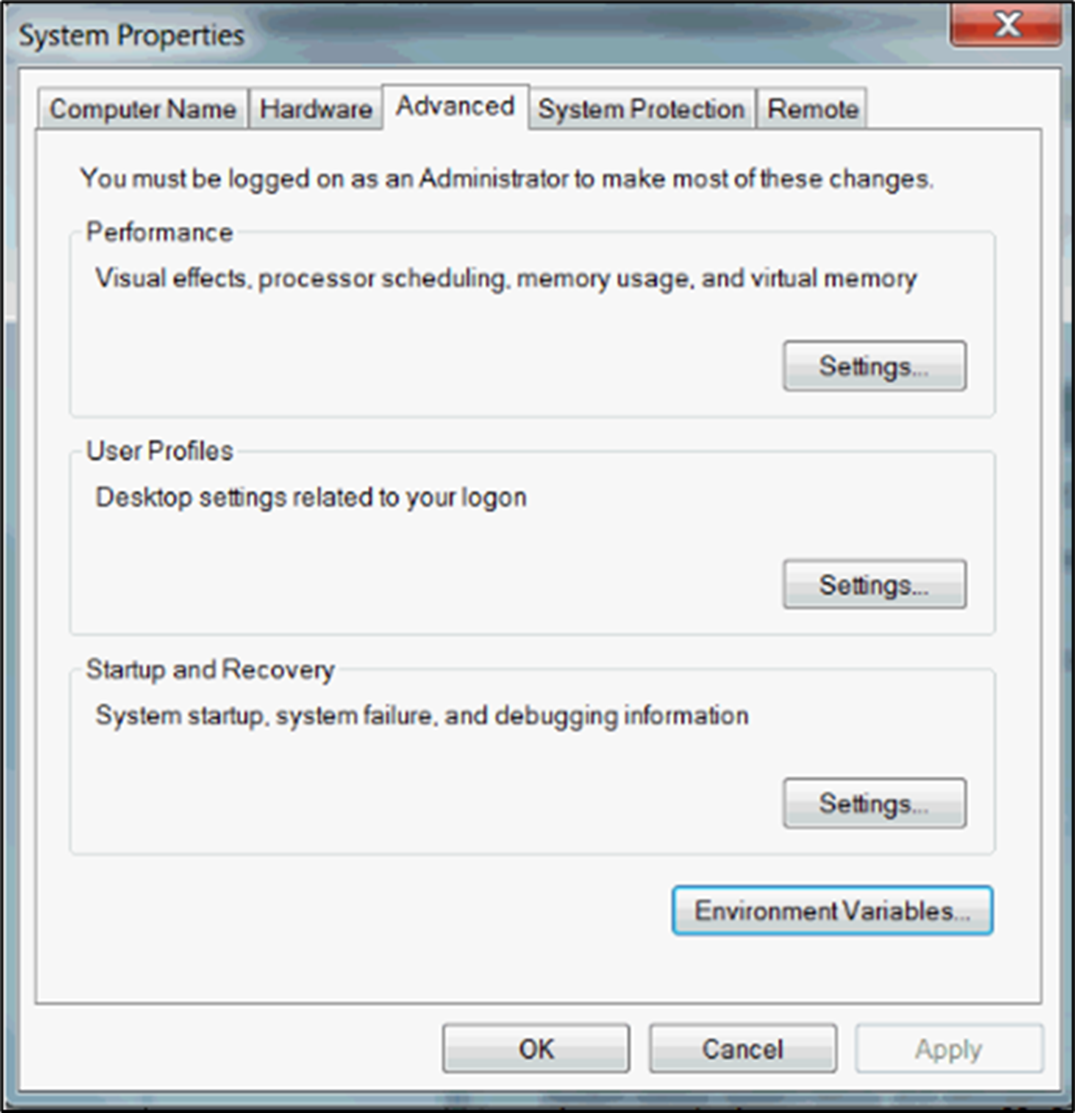
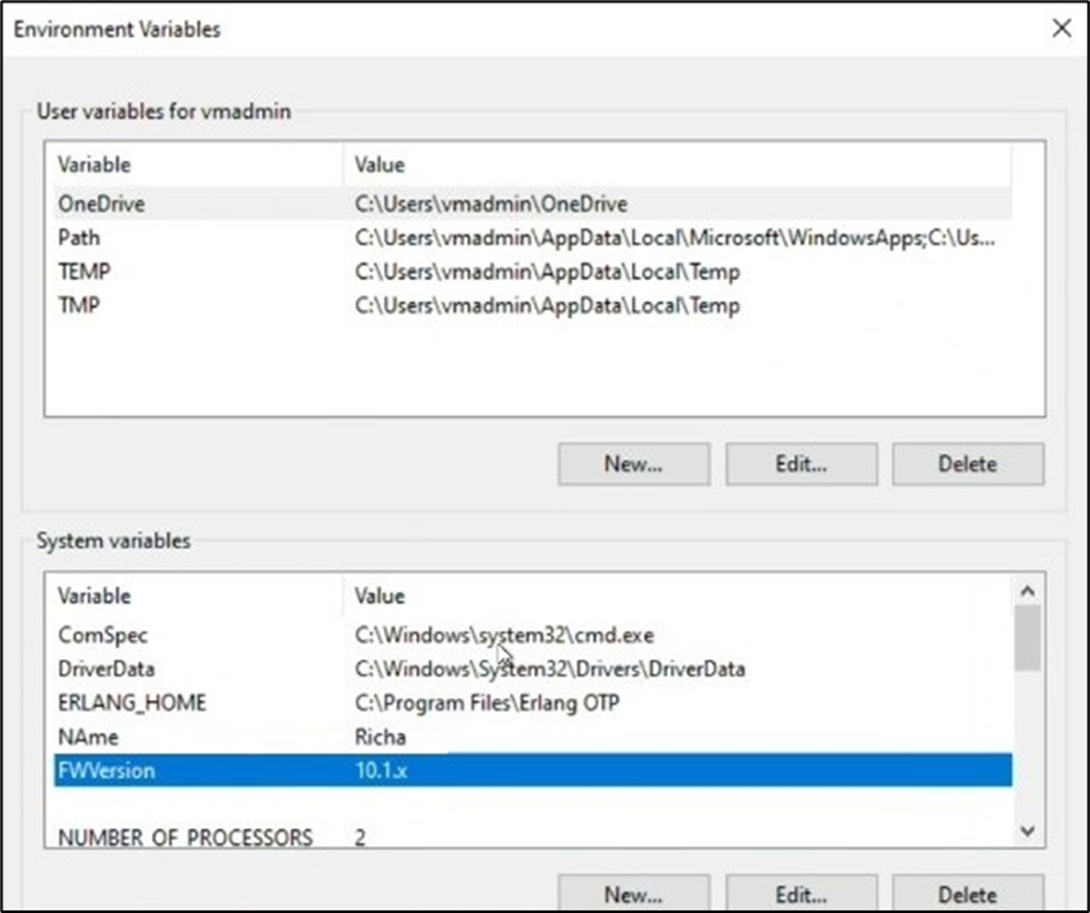
- On the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables. The new variable added by the step will be displayed in the list.
Definition Sample:
You may download the sample definition(s) from the link here and later import them (drag-and-drop) to your FlowWright Process Definition (XML file) or Form Definition (HTML file) page.
Note: Please verify and complete the process steps for any missing configurations, such as file path references and database connections, after the import. Then, save the definition to confirm the changes.
Click here to download the sample file.