persistProcessInstance Step
Description:
This step in the workflow persists the process instance to the database. By design, the process instance is persisted automatically to the database when the instance status is Sleeping, Error, ErrorWait, Aborted, or Completed. This step allows the process instance to persist to the database on demand.
Inputs
- None
Returns
- None
Usage:
Example:
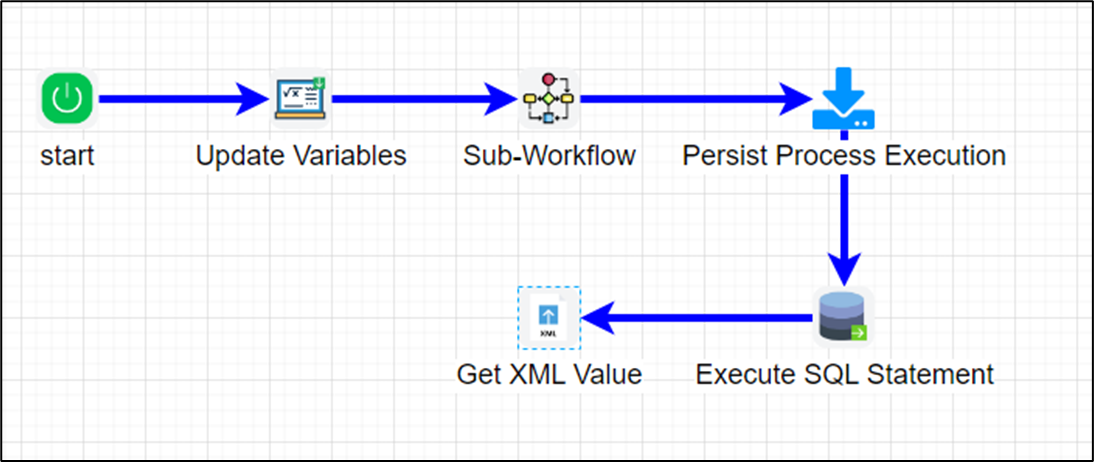
Let’s build and execute the “persistProcessInstanceDef” example.
- Create a new definition called “persistProcessInstanceDef” and open the definition in designer mode.
- Drag the “UpdateVariables,” “subWorkflow,” “persistProcessInstance,” “executeSQL,” and “getXMLValue” steps to the canvas.
- Connect the dots between the “Start” and other steps, as shown above
- Define a variable or a global to store the result.
- Click the “UpdateVariables” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide a name for the step, then click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have the Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the “UpdateVariables” step to configure its “Optional” properties. Click the button to configure multiple variables. A pop-up window appears for configuration. Click the Add Row button to insert an empty row. Enter the variable name and value. Click the Save button. You may add multiple variables using the Add Row button.

- Click the “sub-workflow” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide a name for the step, then select the process definition from the drop-down list. Click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have the Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the “sub-workflow” step to configure its “Optional” properties. Select “Yes” to pass variables from the parent to the child instance. Select “Yes” to pass variables from the child to the process instance. You can configure this setting to pass globals between parent and child instances. Click the Save button.

- Click the button to configure the parent-to-child variable mappings as shown below. Click the Add Row button to insert empty rows. Provide the mapping between sub-process variables and parent process variables or values. Click the Save button. You may insert multiple variable mappings by using the Add Row button.

- Click the button to configure the child-to-parent variable mappings as shown below. Click the Add Row button to insert empty rows. Provide the mapping between sub-process variables and parent process variables or values. Click the Save button. You may insert multiple variable mappings using the Add Row button.

- Click the “persistProcessInstance” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide a name for the step, then click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have the Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the “executeSQL” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide a name for the step. Select the connection string from the drop-down list. Enter the SQL statement. Select the result format as XML or JSON. Click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have the Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the “executeSQL” step to configure its “Optional” properties. If the other database is not the default, provide its name. Provide the variable or global reference to store the value. Select “Yes” to return a single SQL result set. Provide the command timeout value in seconds. Click the button to configure multiple SQL parameters and values. Click the Save button.

- Click the “getXMLNode” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide the XPath expression to query the collection. Provide the variable or global reference to store the XML result. Provide the node reference row from which to retrieve the value. Provide a variable or global to store the collection index. Provide the variable or global reference to hold the XML value. Click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button for the Copilot to add new process steps that match your process description.

- The “Logging” configuration is necessary for documentation and also measures workflow progress and percent complete. This is achieved by configuring the step state and percent fields individually, as shown in the images below. Configure the “Logging” using the following properties.

- Save the process definition, create a new instance, and execute it. This “persistProcessInstance” step persists the current instance in the database as configured.
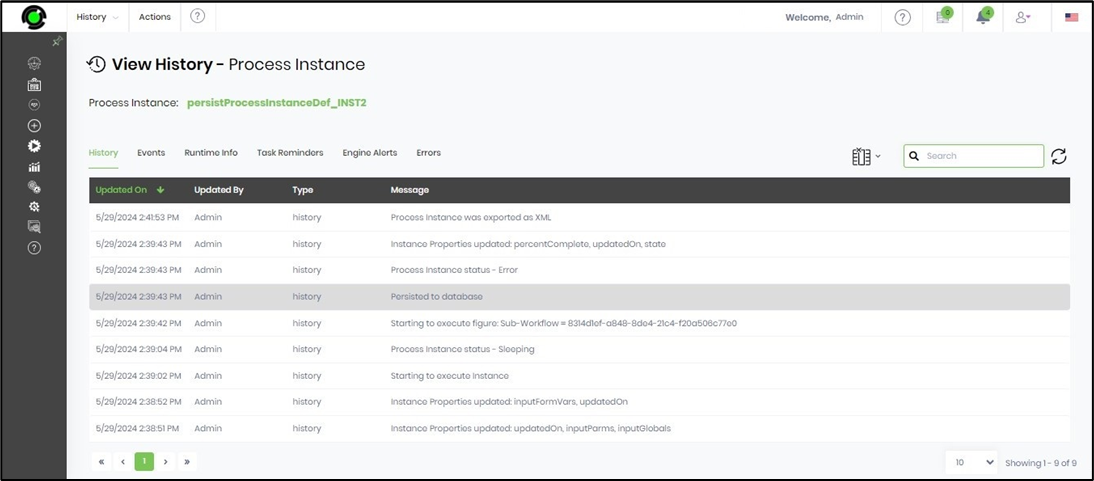
- In this example, the process instance values from the Start step through the “persistProcessInstance” step are recorded in the database. This step allows completion even when the current instance is not yet finished. On the process instance page, select the current process instance and navigate to the View—History menu option. The instance history, including the persistence-to-database event, is displayed in a table on a new page.
Definition Sample:
You may download the sample definition(s) from the link here and later import them (drag-and-drop) to your FlowWright Process Definition (XML file) or Form Definition (HTML file) page.
Note: Please verify and complete the process steps for any missing configurations, such as file path references and database connections, after the import. Then, save the definition to confirm the changes.