start Step
Description:
This step is the first step in any process definition. It starts the process execution.
Inputs
- Variables – define variables for the workflow definition
- Globals – define globals for the workflow definition
- formVariables - manage Form variables
- businessObjects - manage Business Objects
- priority - Set process priority (low, medium, high)
- useSingleIterations - keep only the last execution iteration
- errorDef - execute this process definition when the instance has errors
- abortDef - execute this process definition when the instance is aborted
- completeDef - execute this process definition when the instance completes
- defaultProcessUser - select the default process user to use when the RouteForm, Task steps are directed to an invalid user
Returns
- None
Usage:
Example:
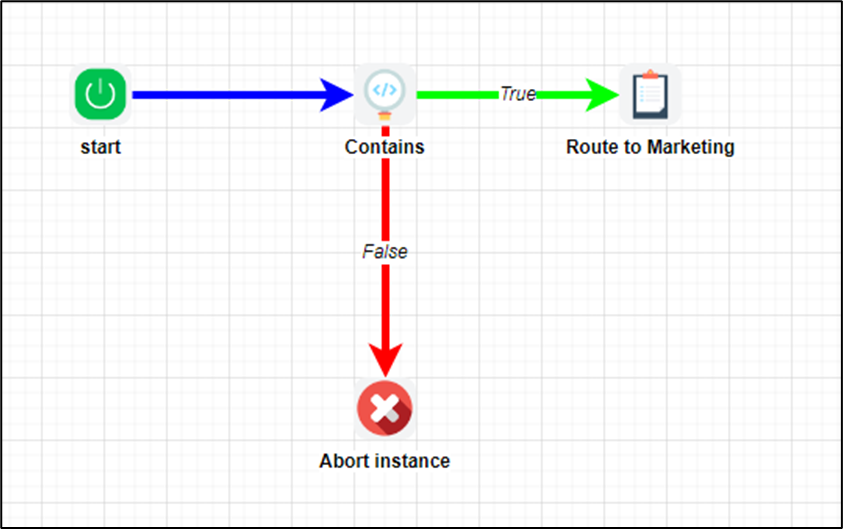
Let’s build and execute the “startDef” example.
- Create a new process definition called “startDef" and open it in Designer mode.
- Drag the “Contains, Task, AbortInstance” controls to the canvas.
- Connect the dots between the “Start” step and other steps, as shown above.
- Click the "Start" step to configure its "Required" properties. Provide a name for the step, then click Save. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the "Start" step to configure its "Optional" properties. Click the button to configure the variables, globals, form variables, and business objects. Select one of the priority values (high, medium, low) from the drop-down list. Select “Yes” to Use a Single Execution Iteration if you want the process instance to retain only the last execution iteration. This is useful when the process instance is designed to loop (n) times to complete the workflow, and only the previous iteration must be retained. By default, the configuration is set to “No,” meaning all iterations are retained. Select the process definition from the drop-down list for the error, abort, and completed workflow status. Click the button to select the default process user. Click the Save button to confirm.

- Click the button to select the default process user. Use the arrow buttons to navigate and select the user. Alternatively, provide a variable or global reference containing the UserID value. The system variable “variable.initiatorID” can also be used. Click the Save button. Note: This configuration is optional. When a default user is configured, the application iterates over the routeToList, attempts to assign a workflow task to each user, checks whether each user exists and is active, falls back to the default process user if configured, logs errors for invalid or inactive users, handles delegated task ownership, and prevents duplicate task creation per user.

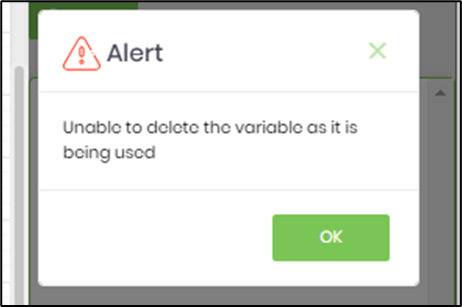
- Click the button to manage variables. All variables defined earlier in the workflow are listed in the table. Enter the variable name, select the data type from the dropdown list, and click the “Add” button to add new variables to the process. Select the variable name and click the “Remove” button to remove the variable from the process permanently. First, select the variable from the list, then click the “Change Type” button to change the variable's data type.
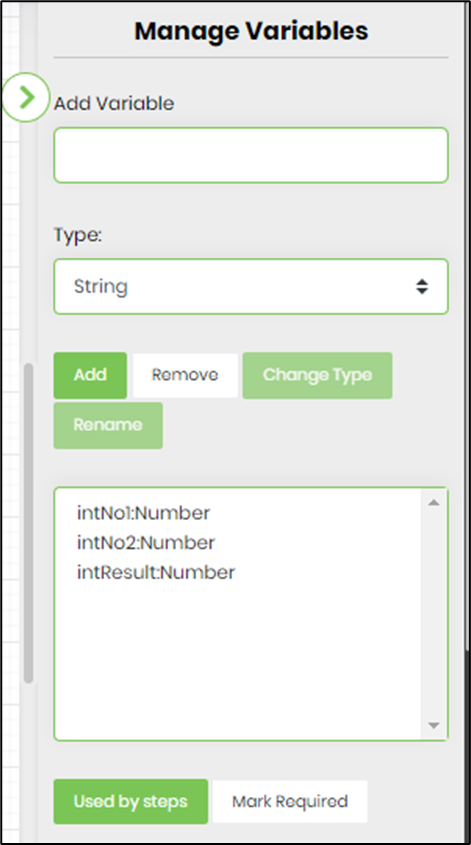
- Select the variable from the list, then click the “Used by steps” button to view all steps that use it. The associated steps are hyperlinked to help track their location when clicked.

- Select the variable, then click the “Mark Required” button to prevent accidental removal. The variable is highlighted in red, and the same button toggles it back to normal.
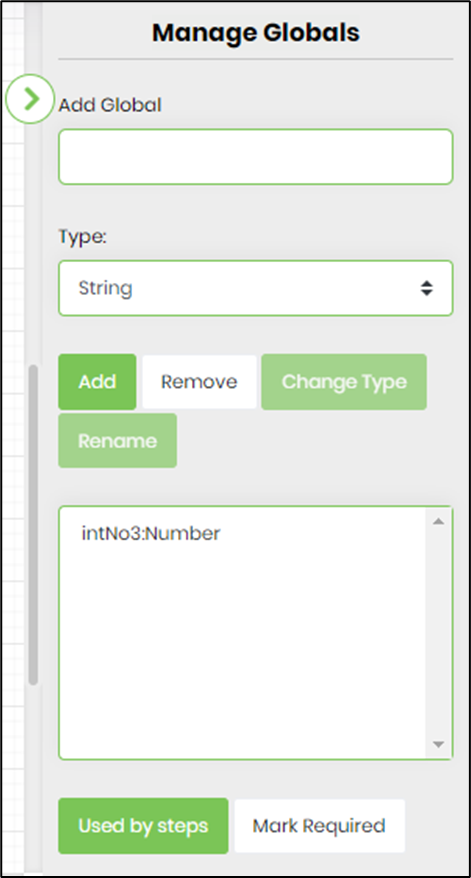
- Click the button to manage globals. All globals defined earlier in the workflow are listed in the table. Provide the global name, select the data type from the dropdown, and click the “Add” button to add a new global to the process. Select the global name, then click the “Remove” button to permanently remove it from the process. First, select the global from the list, then click the “Change Type” button to change its data type. Select the global from the list, then click the “Used by steps” button to view all steps that use it. The associated steps are hyperlinked to help track their location when clicked. Select the global and click the “Mark Required” button to prevent accidental removal. The global is marked in red, and the same button toggles the status back to normal.
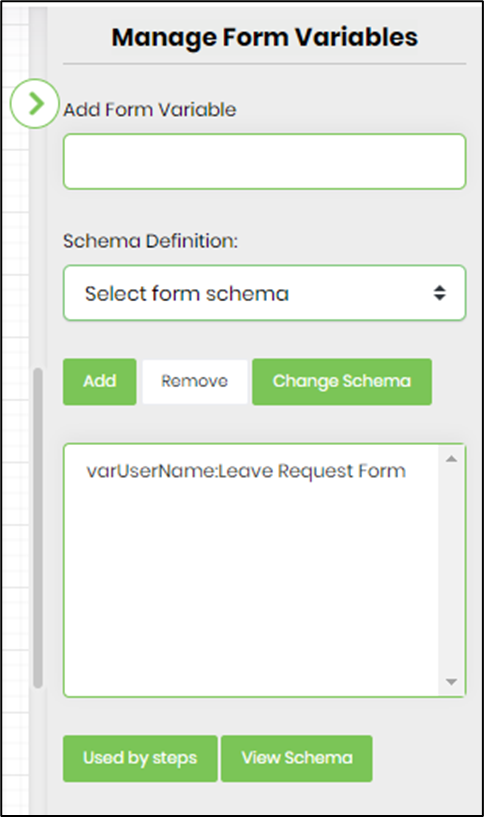
- Click the button to manage form variables. Select the Form Definition from the dropdown list. Enter the variable name, then click “Add” to add a new form variable. Select the variable name from the list, then click “Remove” to permanently remove it. Select the variable name from the list, then click “Change Schema” to map it to another form definition from the dropdown list.
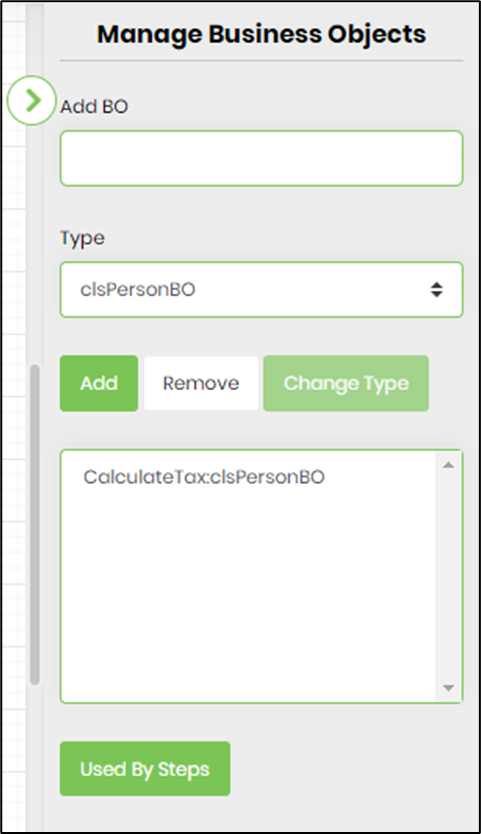
- Click the button to manage business objects (BO). Select the type from the dropdown list. Enter the BO name, then click “Add” to add a new object. Select the BO name from the list, then click “Remove” to permanently remove it. Select the BO name from the list, then click “Change Type” to change the BO type.
- Configure the execution path to follow when the process instance status is 'Abort', 'Errors', or 'Completed'. Use the drop-down list to select an existing process workflow for each status. This configuration is optional, but can optimize the real-time completion of the process instance.

- Save the process definition, create a new instance, and execute it. Render the process instance. Click the process step to view its properties. The “Start” step should initiate execution as configured.
Use the “AI Predict” feature.
- Click the "Start" step to configure its "Required" properties, then click the AI Predict button.

- A pop-up window appears to configure the Copilot's Predict Next Steps feature. Enter the step count value to generate. Enter the text description of the context. Then click the Predict button.

- The predicted steps are listed below. You can use the checkbox to skip unnecessary steps. Click the button to add the expected list of steps to the existing workflow, branching from the Start step.

- The AI-predicted steps are connected as follows.

Definition Sample:
You may download the sample definition(s) from the link provided and later import them (drag-and-drop) into your FlowWright Process Definition (XML file) or Form Definition (HTML file) page.
Note: Please verify and complete the import process steps for any missing configurations, including file path references and database connections. Then, save the definition to confirm the changes.