FlowWright engines have various configuration settings that are used by each engine to function. You can view and modify these settings by navigating to Status → Settings → Configuration.
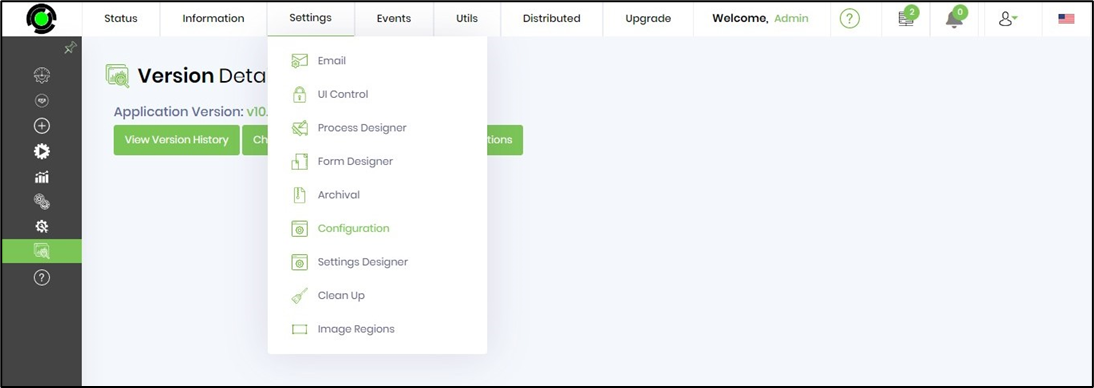
Navigate to Application Settings to view / change the configuration.
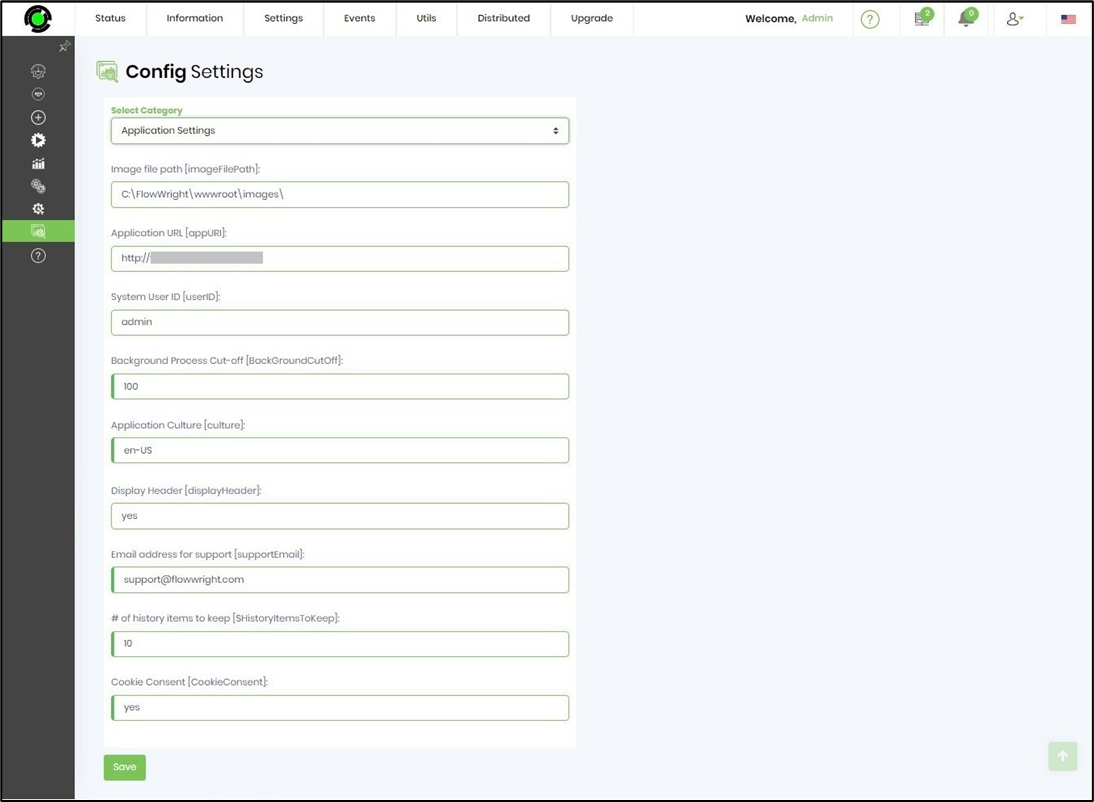
Configuration settings are read by the engines at start up time and every 5 minutes. Engines are able to auto configure them selves at runtime based on the configuration provided.
Workflow Engine Service
All date/times are stored within the database as UTC and displayed based on local timezone of the user.
Note: Engine runtime data are in ISO + UTC format.
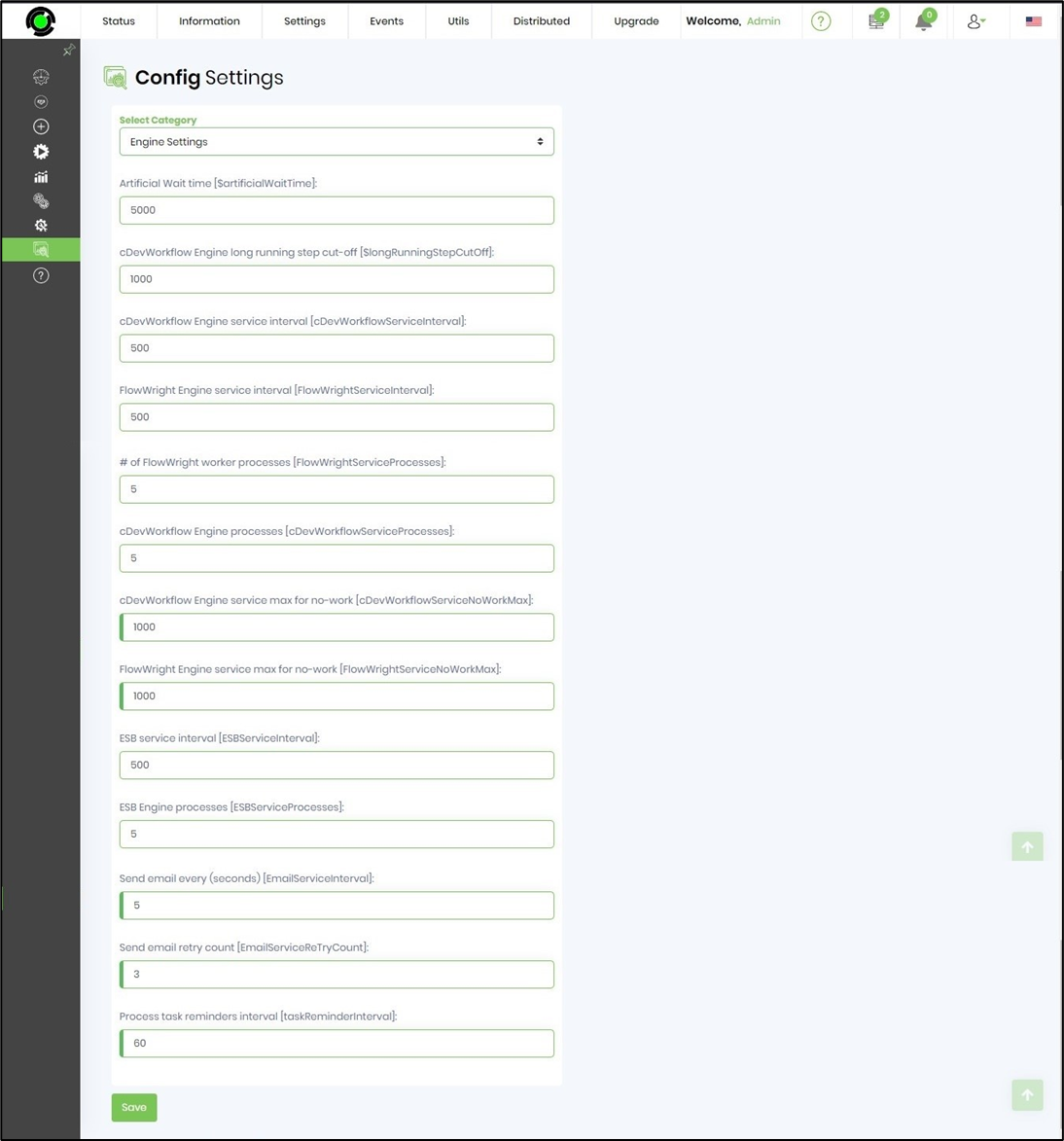
Artificial Wait time - if the workflow goes into an endless loop or the # of continuously executed steps are equal to = Engine long running step cut-off limit, then the engine automatically puts the workflow instance into a 100 second wait.
Engine service interval - this interval is used to determine how often to check for work from the database, with a configuration of 500ms, the engine checks for work every 1/2 second.
Engine processes - maximum # of child processes to launch to process workflow, by default its 5 child processes, increase this based on resources of the environment.
Engine service max for no-work - this value is used if the engine has no work to perform, normally engine would check for work every 1/2 second, if there's no work to be done, then the engine will start checking every 1 second. Soon as there's work to be done, then it will change to use the 1/2 second check.
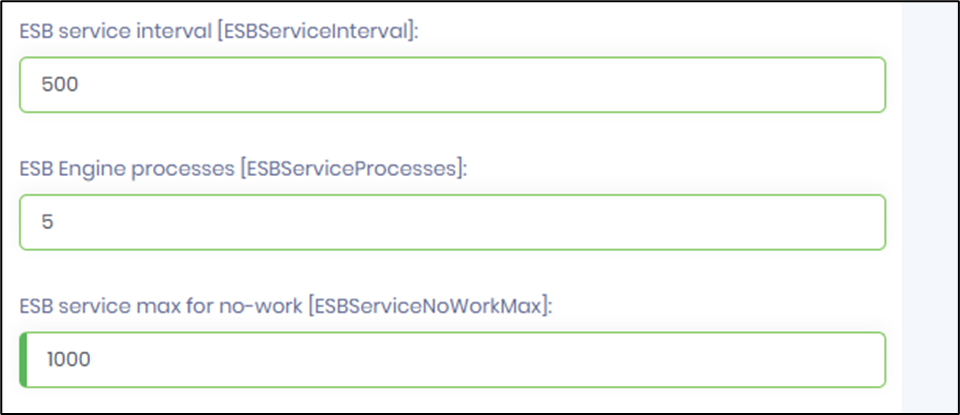
ESB Engine Service
The ESB engine has similar settings as the workflow engine.
Email Service
The email services uses the below settings to send and retry emails.

Archival Service
The archival service runs every hour but processes archival based on the configuration values that are configured for archival.

Statistical Service
Statistical service runs daily and collection statistics on processes.
Trigger Service
Trigger service uses the configuration from each of the triggers that are configured within FlowWright.
DFS Service
Distributed file system service synchronizes files across distributed servers using the following configuration within FlowWright
