XmlToXls Step
Description:
This step converts the XML data into an XLS file.
Inputs
- xmlVariable – variable or global that holds the XML data
- xlsFilePath – variable or global that holds the output file path on the server
- xmlNodeName – mention XML node to parse or consider the XML data between <root> and <\root> tags to parse by default
- workSheetName - renames the worksheet with this name (not mandatory)
- writeColHeadings - write column names (On / Off)
Returns
- True – step executed successfully
- False – step failed to execute
Usage:
Example:
Let’s build and execute the “XmlToXlsDef” example.
- Create a new definition called “XmlToXlsDef” and open the definition in designer mode.
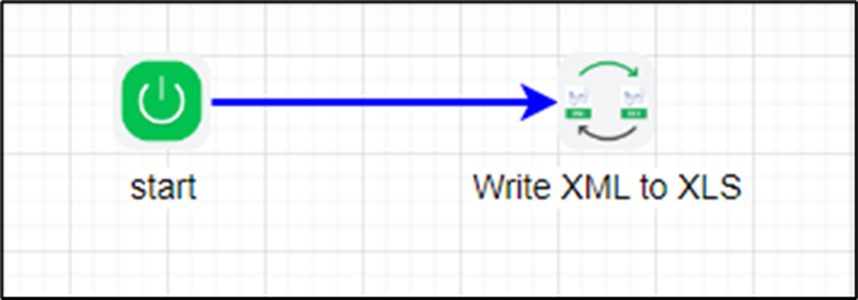
- Drag an “XmlToXls” step to the canvas.
- Connect the dots between the “Start” and “XmlToXls” steps, as shown above.
- Define a variable or a global to store the result.
- Click the “XmlToXls” step to configure its “Required” properties. Provide a name for the step. Provide a variable or global that contains the XML data. Provide a variable or global that contains the XLS file path. Click the Save button. Note: Click the "AI Predict" button to have the Copilot add new process steps that match your process description.

- Click the “XmlToXls” step to configure its “Optional” properties. Provide the XML node information for the XML data. Provide the worksheet name. Select “On” to include column names in the worksheet.

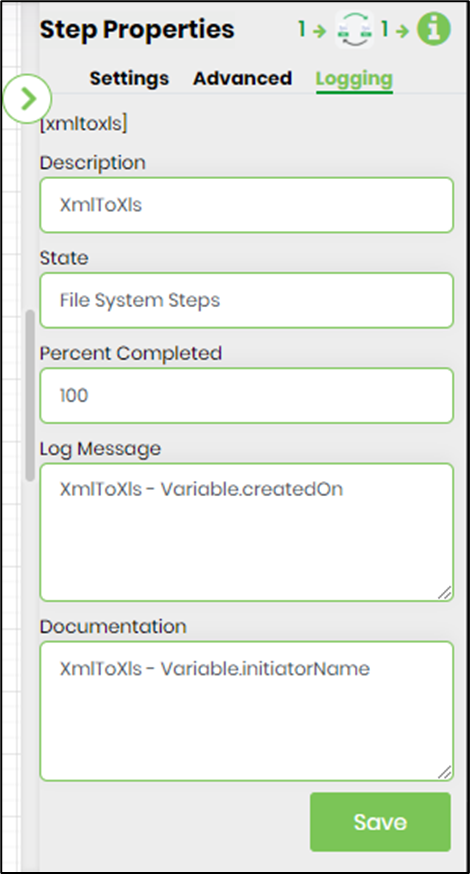
- The “Logging” configuration is necessary for documentation and also measures workflow progress and percent complete. This is achieved by configuring the step state and percent fields individually, as shown in the images below. Configure the “Logging” using the following properties.
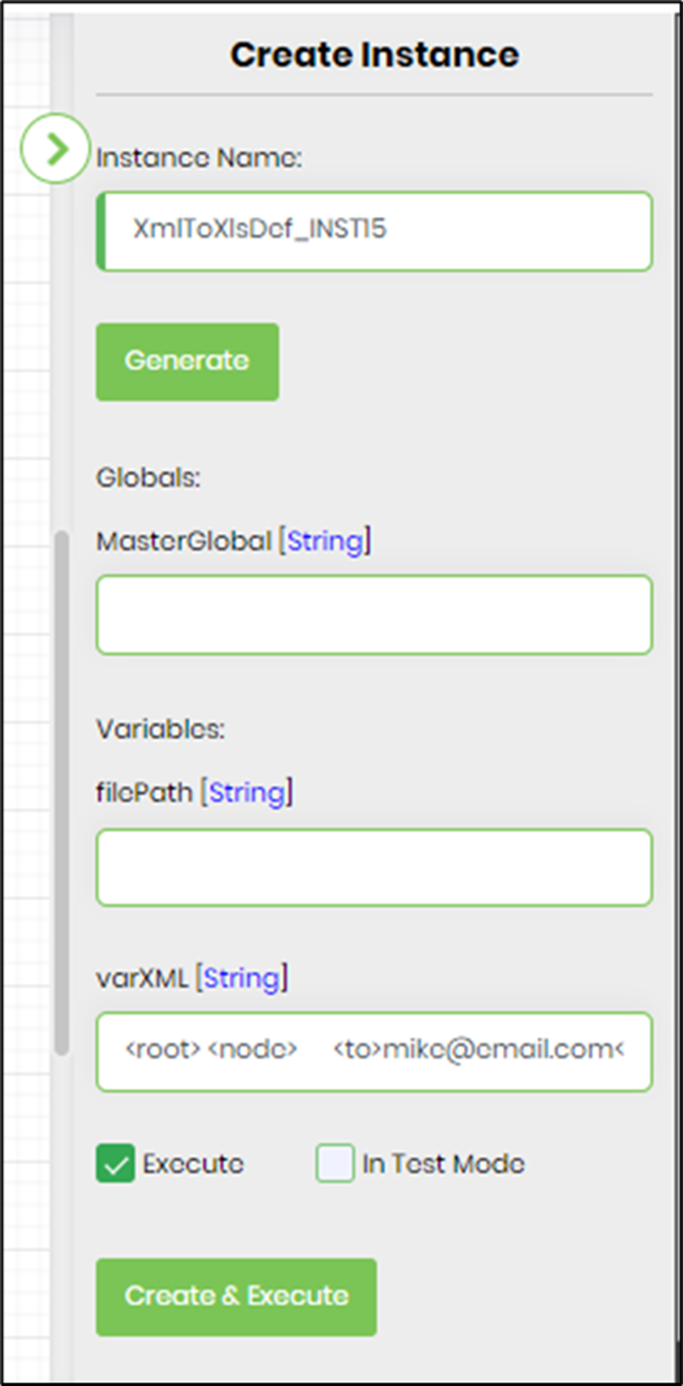
- Generate a new process instance. Initialize the varXML variable with the sample XML data shown below. The step shall process the raw XML data between the <root> and <\root> elements, or a specific node configured above in Advanced - XML nodes to be processed. This XML node can also refer to the root node (root) or a specific node (node) in the XML data. Copy and paste the sample XML data into the xmlVar variable to initialize it. Typically, the varXML variable is initialized by other XML steps, such as executesql and generatexml, in a process workflow. Execute this new process instance.
<root> <node> <to>mike@email.com</to> <from>flowwright@support.com</from> <heading>New social handle</heading> <body>Hi! We're here on Instagram now. Let's connect!</body> </node> <book id='bk101'> <author>Gambardella, Matthew</author> <title>XML Developer's Guide</title> <genre>Computer</genre> <price>44.95</price> <publish_date>2000-10-01</publish_date> <description>An in-depth look at creating applications with XML.</description> </book> <node> <to>lowry@email.com</to> <from>flowwright@support.com</from> <heading>New social handle</heading> <body>Hi! We're here on Instagram now. Let's connect!</body> </node> </root>
- Execute the new process instance.
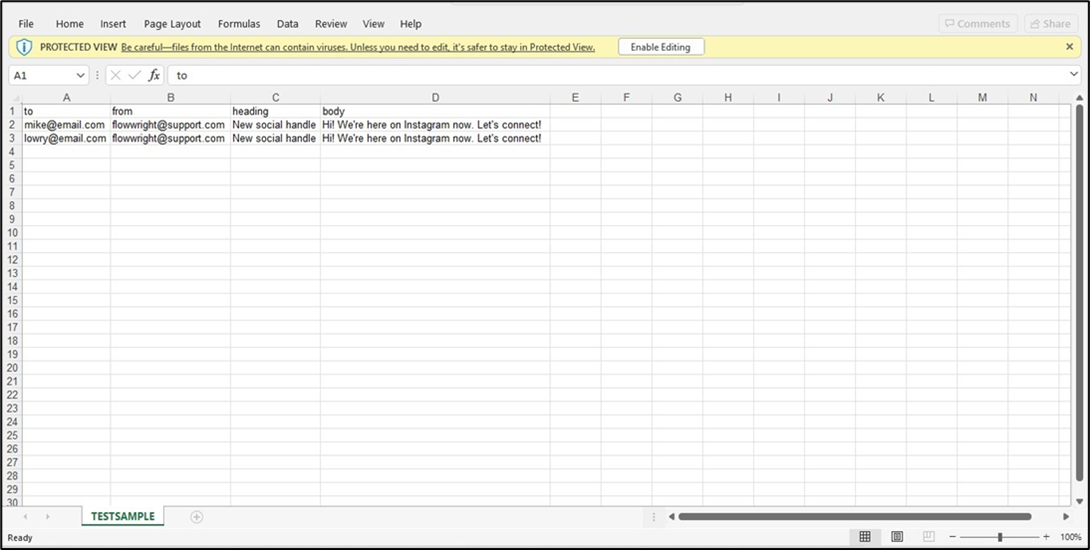
- The step shall transform the XML data into an XLS file on the server. The default Sheet1 worksheet is renamed to the configured value (TestSample). Download the XLS file and use the appURI and filePath variable values from the step property.
Definition Sample:
You may download the sample definition(s) from the link here and later import them (drag-and-drop) to your FlowWright Process Definition (XML file) or Form Definition (HTML file) page.
Note: Please verify and complete the process steps for any missing configurations, such as file path references and database connections, after the import. Then, save the definition to confirm the changes.
Click here to download the sample file.